Green area of the SNAM plant
SNAM system make with IrriRT
Green area SNAM plant
Irrigation system serving green areas
The project involved the irrigation system serving green areas within the SNAM plant in the Tarsia area (in Calabria). The total area is approximately 12 Ha and is made up of green lawn flowerbeds. The terrain is mostly flat.
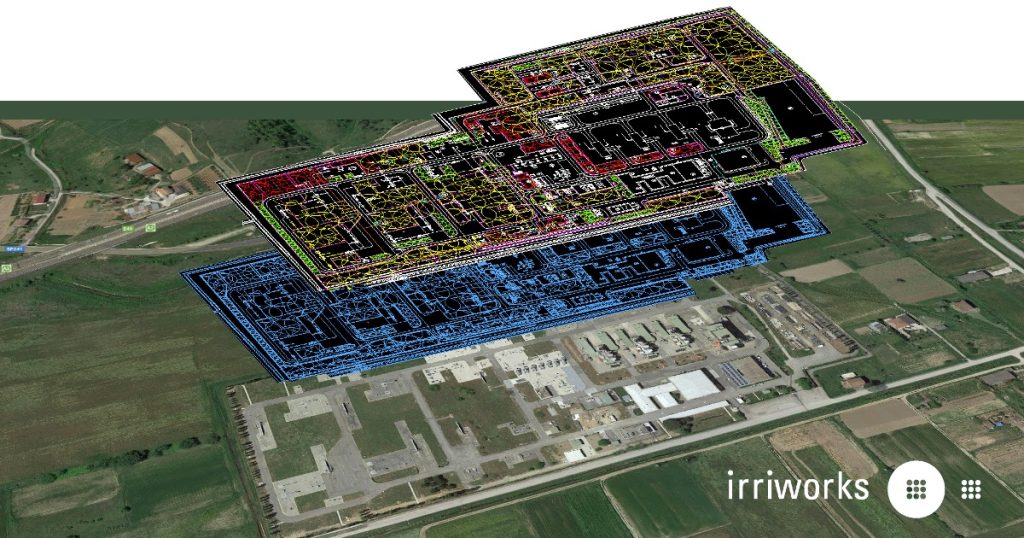

The Project
Through a well, the water is collected in a storage tank which hydraulically separates the constant flow rate coming from the well and the irrigation system which requires greater flow rates and shorter durations. The pump which, from the accumulation tank, supplies the irrigation system for the different shifts has been sized so as not to exceed the compensation volume.
The plant is made up of more than 3000 m of DN90 main pipelines and problems of various crossings for existing works have been addressed. Several sectioning solenoid valves have been inserted in order to divide the main network and control which sections to engage and which to exclude.
In order to manage the 19 shifts, made up of groups of sectors and chosen so as to balance the flow rate around an established average value in the different shifts, 56 solenoid valves and two control units have been provided to control the valves and the pump in two groups .
Project Objective
The shift calendar has been developed in such a way as to:
- have a similar flow rate for each turn
- cover watering within a day
- the equivalence between the volume entering and exiting the accumulation tank has been verified
- simulate additional hydraulic conditions.
The turf of the green areas is irrigated with more than 500 pop-up sprinklers (dynamic and static), while the perimeter part with hedges and shrubs is irrigated with drip lines (self-compensating). The rainfall overlap of the wet circles and the uniformity of distribution were verified. More than 40 pressure reducers have been inserted to keep the pressure below certain limits in some areas of the system (especially for the drip part which requires lower pressures to function).
In the project, various scenarios were evaluated (some discarded due to lack of uniformity, efficiency and balancing of flow rates per shift), and finally the one was chosen that reaches the required daily requirement to irrigate the entire surface, which has an adequate rainfall intensity, an acceptable uniformity and is compatible with the compensation, volume and flow rate conditions of the power supply.


